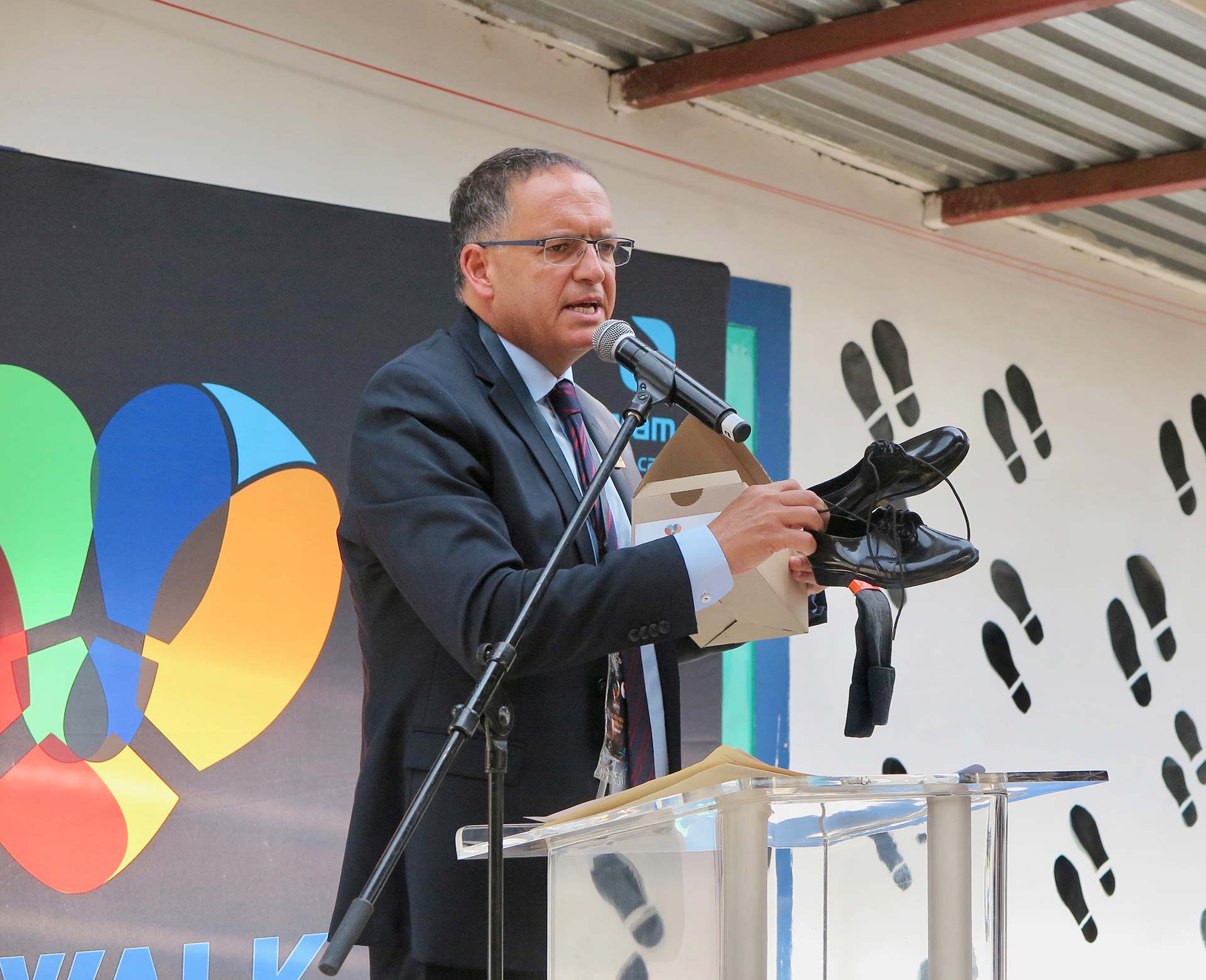
Recycled hospital drip bags to be made into 25 000 pairs of school shoes for SA learners this year
Drickus Maartens • February 6, 2020
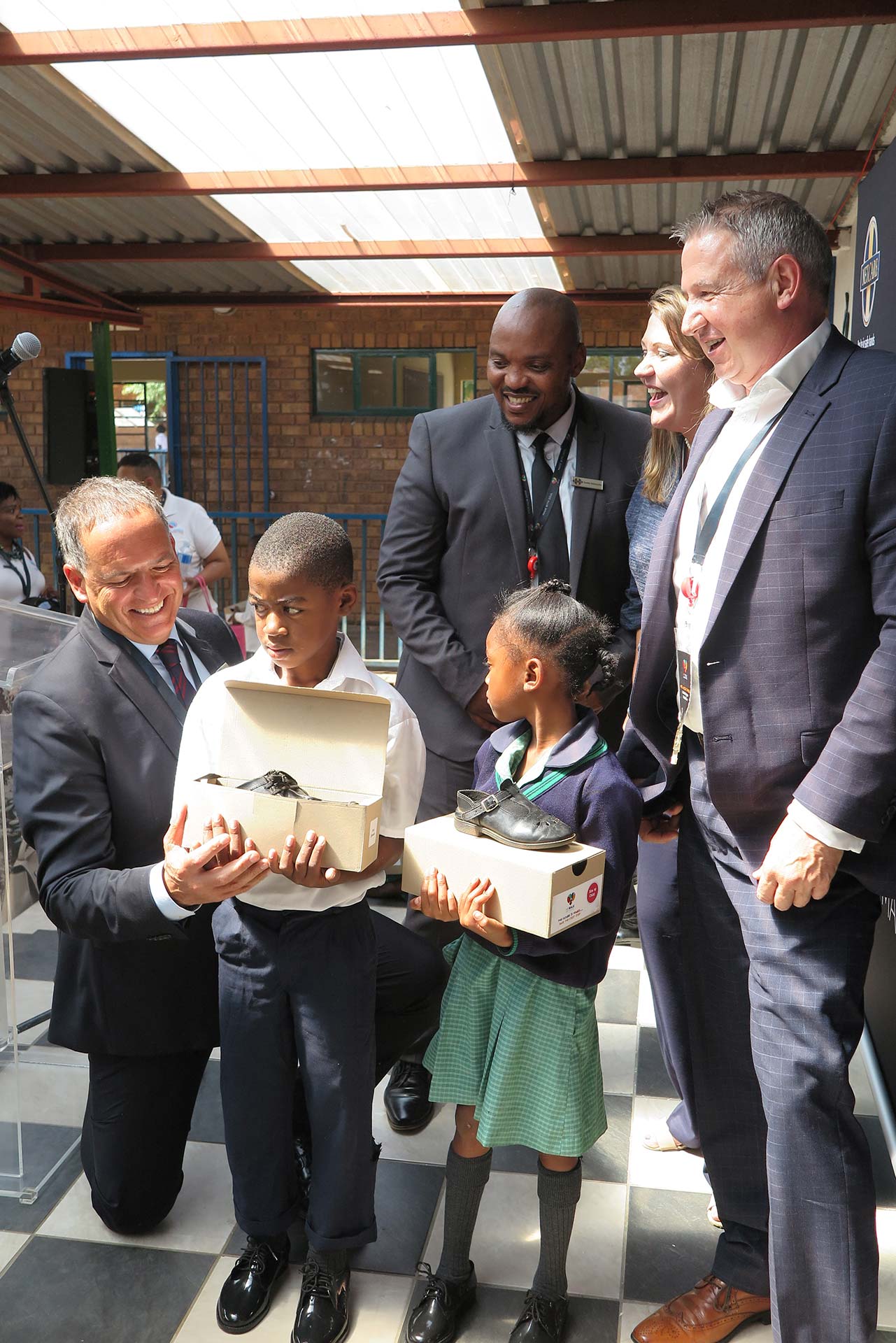
Adcock Ingram Critical Care (AICC) and Netcare representatives were thrilled to hand over brand new school shoes made from recycled uncontaminated PVC IV drip bags, and to engage with learners at Chivirikani Primary School at the launch of the companies’ My Walk initiative. From left to right were Mr Colin Sheen, MD of AICC; Dr Nceba Ndzwayiba, director transformation at Netcare; Dr Claudia Manning, member of the Adcock Ingram board and chairperson of the board’s social, ethics and transformation committee; and Advocate Kgomotso Moroka, a non-executive Netcare board member and chairperson of the board’s social and ethics committee.
My Walk initiative turns non-hazardous healthcare waste into useful footwear
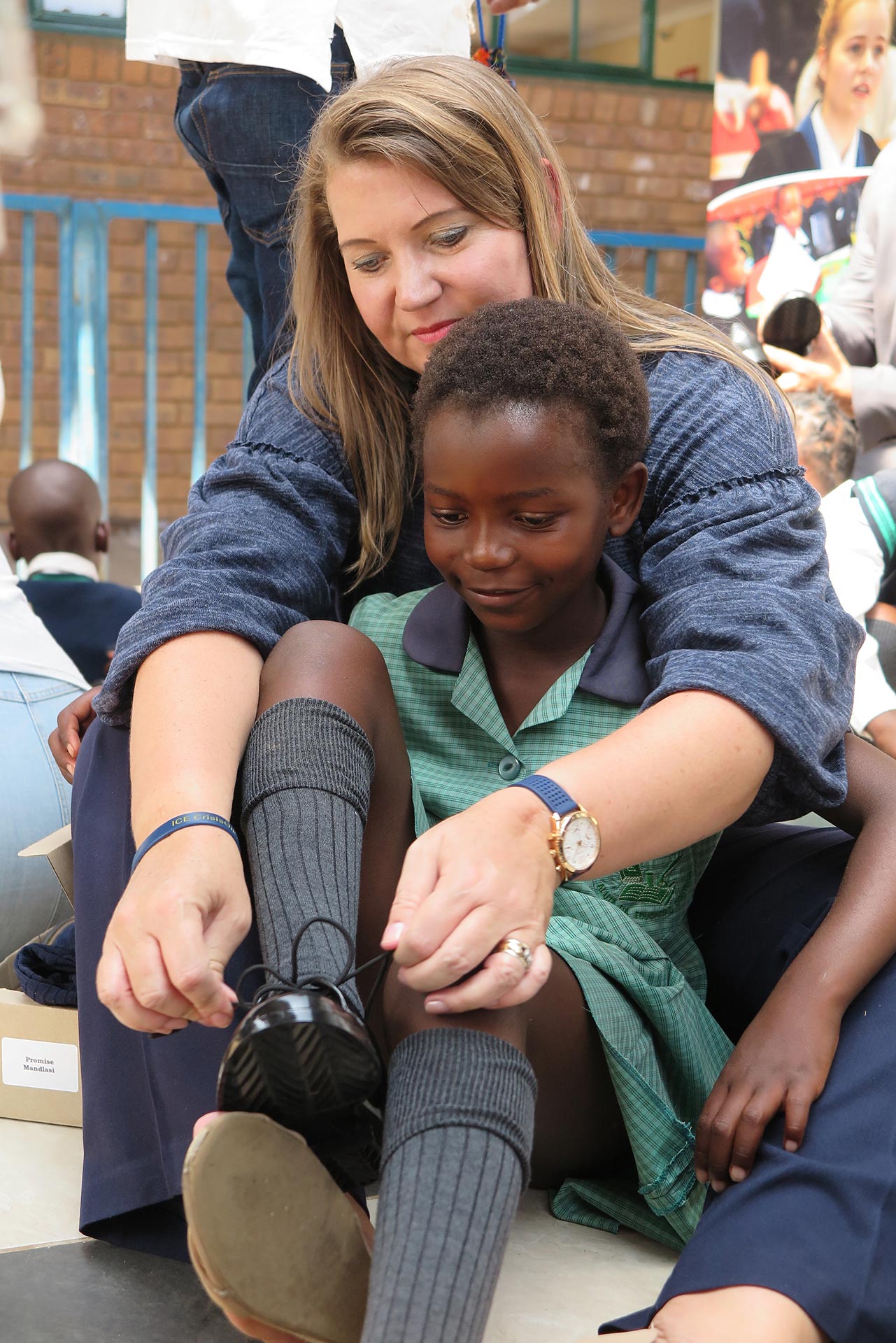
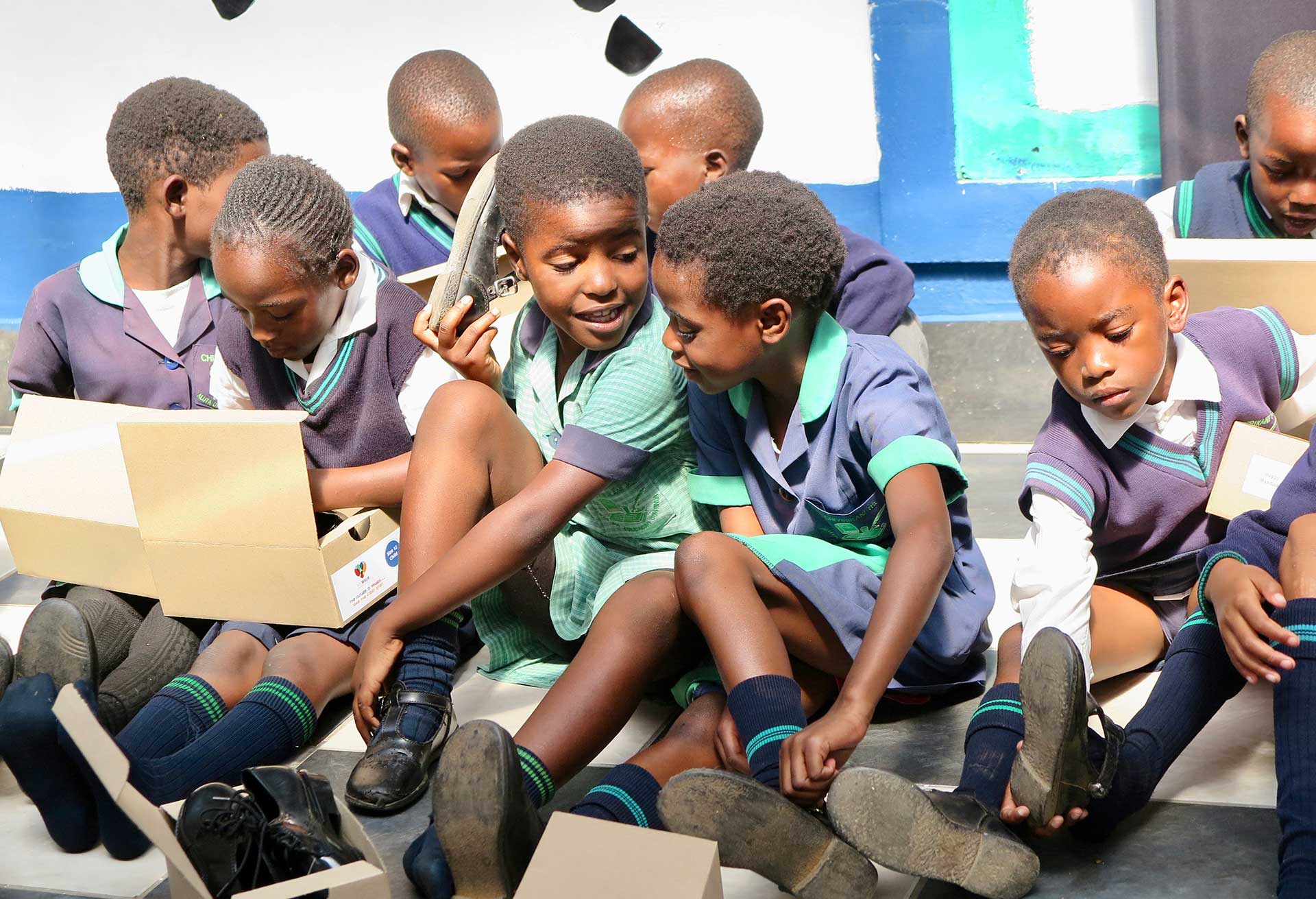
More than 1 300 primary school learners of Chivirikani Primary School in Katlehong, south-east of Johannesburg, yesterday received a pair of brand new school shoes made from non-hazardous, recycled PVC healthcare waste products. This means that these young learners will attend school this year in improved safety and comfort while proudly walking in shoes that have contributed towards reducing the country’s landfill waste burden and emission of greenhouse gasses.
A further 25 000 learners around the country will receive shoes during 2020 through the My Walk initiative, an innovative partnership between Netcare
and Adcock Ingram
Critical Care that is turning used, uncontaminated PVC intravenous drip bags, oxygen masks and associated tubing into shiny new school shoes, made from 100% recycled material. The school shoes themselves are also 100% recyclable, with the exception of the laces.
A prototype of the school shoes was tested at three schools in 2019, in order to get first hand feedback from learners on the design and comfort. The final unisex shoe design took into consideration the valuable feedback received from the learners. One of the participating schools was Chivirikani Primary School, and it was therefore decided, in consultation with the school, to launch the My Walk initiative at its premises and distribute the first batch of fully recycled school shoes to learners at the school.
Innovative, sustainable solutions for the long term
Speaking at the launch of the My Walk initiative, the Chief Director: National and Provincial Communication in the Ministry of Basic Education, Mr Elijah Mhlanga, welcomed the initiative, saying: “School shoes are a basic necessity, and if learners do not have adequate footwear, this can introduce ongoing obstacles to their education including bullying and harassment at school. Having school shoes can enhance the schooling experience for learners. Many learners unfortunately still walk long distances to and from school without shoes, facing a daily threat of sustaining cuts and infections.”
Chivirikani Primary School principal, Mr Christopher Maluleke, added: “School shoes mean more than just completing the uniform. When children don’t have shoes, it can affect their personal dignity and self-esteem, which may negatively impact their school experience, academic performance and potentially hold them back from participating in games and sports. Wearing fit for purpose school shoes can help bolster children’s confidence and self-esteem and have an all-round positive effect on their journey of development and learning, so that they can be better equipped for the future.”
All-round benefits
Chief executive officer of Netcare, Dr Richard Friedland, explains: “We found ourselves with tonnes of high-quality PVC waste, as drip bags, oxygen masks and associated tubing can only be used once in a medical context. In the past, these used, non-hazardous and uncontaminated products ended up at landfills.”
“The My Walk partnership is an example of embracing a circular economy. It shows how a green solution can fulfil a material need for a business while simultaneously benefitting society – in this case by supporting education, job creation and enterprise development,” explains Dr Friedland.
Adcock Ingram Critical Care managing director, Colin Sheen adds: “Our partnership with Netcare in the My Walk initiative demonstrates the meaningful and wider impact that an innovative approach to solving business challenges can have. With nine more Netcare hospitals soon joining the 12 hospitals which are already participating, we are excited about increasing the number of shoes manufactured significantly over the next few years.”
Furthermore, there is potential to exponentially expand the number of school shoes that can be produced if other private and public sector hospitals join us in this worthy initiative,” notes Sheen.
“It is so rewarding for us at Adcock Ingram Critical Care and Netcare to be part of the My Walk initiative. We encourage the learners of Chivirikani primary school and other schools which will benefit from the initiative to take advantage of educational opportunities, and hope that their new school shoes will assist them on this journey,” Sheen and Dr Friedland conclude.

Colorectal cancer, one of the most prevalent yet preventable cancers, can develop in the colon or rectum, often starting as small polyps that can quietly become malignant if left unchecked. Dr Mpho Ramabulana, a colorectal surgeon and gastroenterologist at Netcare Akasia Hospital, underscores the life-saving power of vigilance and the importance of early detection.

The lives of millions of South Africans with a litany of rare diseases can be vastly improved, and even saved, by addressing challenges in identifying, studying and treating their conditions. With Rare Disease Day on the 28th of February 2025, the Rare Diseases Access Initiative (RDAI) is driving an evolution of the country’s healthcare, through innovative strategies to better care for over 4.2million people living with an estimated 7000 rare diseases. “As our healthcare system faces significant changes in the years ahead, it is vital that we also advocate for people living with rare diseases in South Africa, especially those with limited healthcare access,” said Kelly du Plessis, CEO of Rare Diseases South Africa (RDSA), a member of RDAI. “As part of our ongoing research and awareness efforts, RDAI has conducted an initial analysis of the incidence and prevalence of rare diseases within the country.” This research will assist in improving access to healthcare, policy development, and patient advocacy, while giving critical insight into the challenges faced by patients. “According to research, some rare diseases affect fewer than 1 in a million people, while others, such as Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, and haemophilia, have a more recognisable prevalence,” says Dr. Helen Malherbe, RDAI lead researcher on rare disease prevalence data. “Many conditions are undetected, underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed, with too many having no information available about them at all.” The RDAI was formed in 2019 to promote a more favourable environment for those impacted by rare diseases in South Africa. Participants include Ampath, the Board of Healthcare Funders (BHF), Discovery Health, Genetic Counsellors South Africa (SASHG), the Government Employees Medical Scheme (GEMS), Health Funders Association (HFA), Medihelp, Medscheme, North-West University (NWU), Rare Diseases South Africa (RDSA), the South African Medical Association (SAMA) and The South African Medical Technology Industry Association (SAMED). The Council for Medical Schemes (CMS) participates as an observer. In the same year, Rare Disease International signed a memorandum of understanding with the World Health Organisation leading to an international rare disease policy framework. In 2021, the United Nations General Assembly moved to adopt a resolution recognising 300 million people living with rare diseases worldwide. “A general lack of awareness and delayed diagnosis remain major hurdles for those affected by rare diseases. Policymakers and healthcare stakeholders need to prioritise access to treatment, diagnosis, and support for rare disease patients,” says Bada Pharasi, CEO of IPASA, “Through this initiative, working collaboratively with stakeholders at every level of the healthcare supply chain, we can bring real and meaningful change to those affected, including family members and care givers, through smart and efficient strategies.” The globally agreed definition of a rare disease is any medical condition with a specific pattern of clinical signs, symptoms, and findings that affects fewer than or equal to 1 in 2000 persons in a population. “Most are genetic, and some are inherited and passed down in families,” Malherbe says. “Some affect only the patient’s genetic recipe, while others may be acquired during life due to infection, trauma, or environmental effects. For many, the cause is still unknown. “These conditions mainly affect children, as they are largely incurable and many are life-threatening. Some require specialised and co-ordinated care, some have limited and expensive treatment options, while others have no information or effective treatments at all,” she adds. The RDAI is calling for a patient-centred care model built on equitable access, transparency and efficiency. Naturally, this model calls for the open participation of patients, the healthcare industry, health professionals, and the Government. “The most critical elements are robust diagnosis standards, improved access to treatment, data collection and management, co-ordination of care, measurement of outcomes and ongoing collaborative research,” du Plessis says. “We need to establish rare disease advisory committees, map gaps and opportunities, establish system requirements, create a roadmap and plan a phased implementation with clear timelines.” The RDAI states that these policy development steps would be a start in quantifying the disease burden and defining standards of care. This would be followed by building and strengthening the capacity to facilitate appropriate diagnosis, treatment, continuity and data monitoring. Thoneshan Naidoo, Chief Executive Officer of the Health Funders Association noted that, “We appreciate the unique opportunity provided by RDAI which enables stakeholders across the industry to work together and identify strategies that improve equitable access to the appropriate diagnosis, treatment and healthcare services for rare disease patients, in an affordable and sustainable manner, taking account of the other pressing needs across the healthcare system.” “True innovation in healthcare is only possible through partnerships and joint advocacy efforts that raise awareness and improve access to treatment. Our long-term goal is the development of a rare diseases policy framework and guidelines for coordinated care,” says Pharasi. “Our members are united in the commitment to unlocking improved patient outcomes and improving access to services and robust health needs assessment facilities.” he concludes. About RDAI The Rare Diseases Access Initiative (RDAI) is dedicated to advocating for improved healthcare access, policy development, and patient support for those affected by rare diseases in South Africa. The initiative brings together key healthcare stakeholders, including pharmaceutical associations, funders, genetic specialists, and patient advocacy groups, to drive impactful change. About RDSA Founded in 2013, Rare Diseases South Africa (RDSA) is a non-profit organisation advocating to ensure that people living with rare diseases and congenital disorders experience greater recognition, support, improved health service and better overall quality of life. Started out of personal need following the diagnosis of organisation founder, Kelly du Plessis' son, it became evident that there was a lack of awareness and support for rare diseases in general in South Africa. About IPASA The Innovative Pharmaceutical Association South Africa (IPASA) is a voluntary trade association representing 24 leading pharmaceutical companies committed to research, development, and innovation. Our mission is to drive healthcare advancement by advocating for policies that improve patient access to safe, high-quality, and affordable medicines.